
Welcome, we are here to make your work easy, to save your time. Now you can spend time with your loved ones on your holidays. You don’t have to go and buy goods from market, Just make a list and send it to us. you will get your product soon with affordable price.



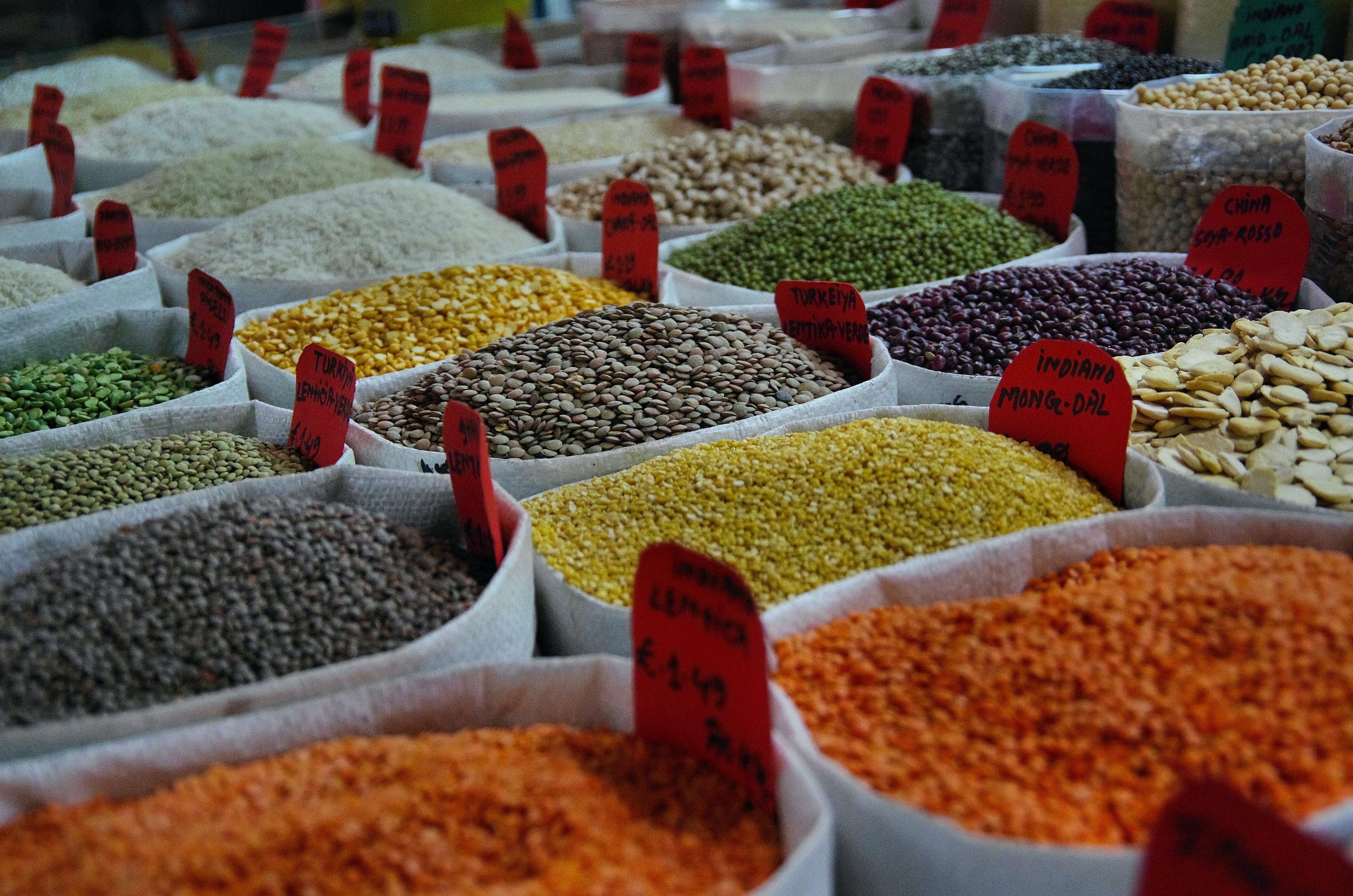
for example:-
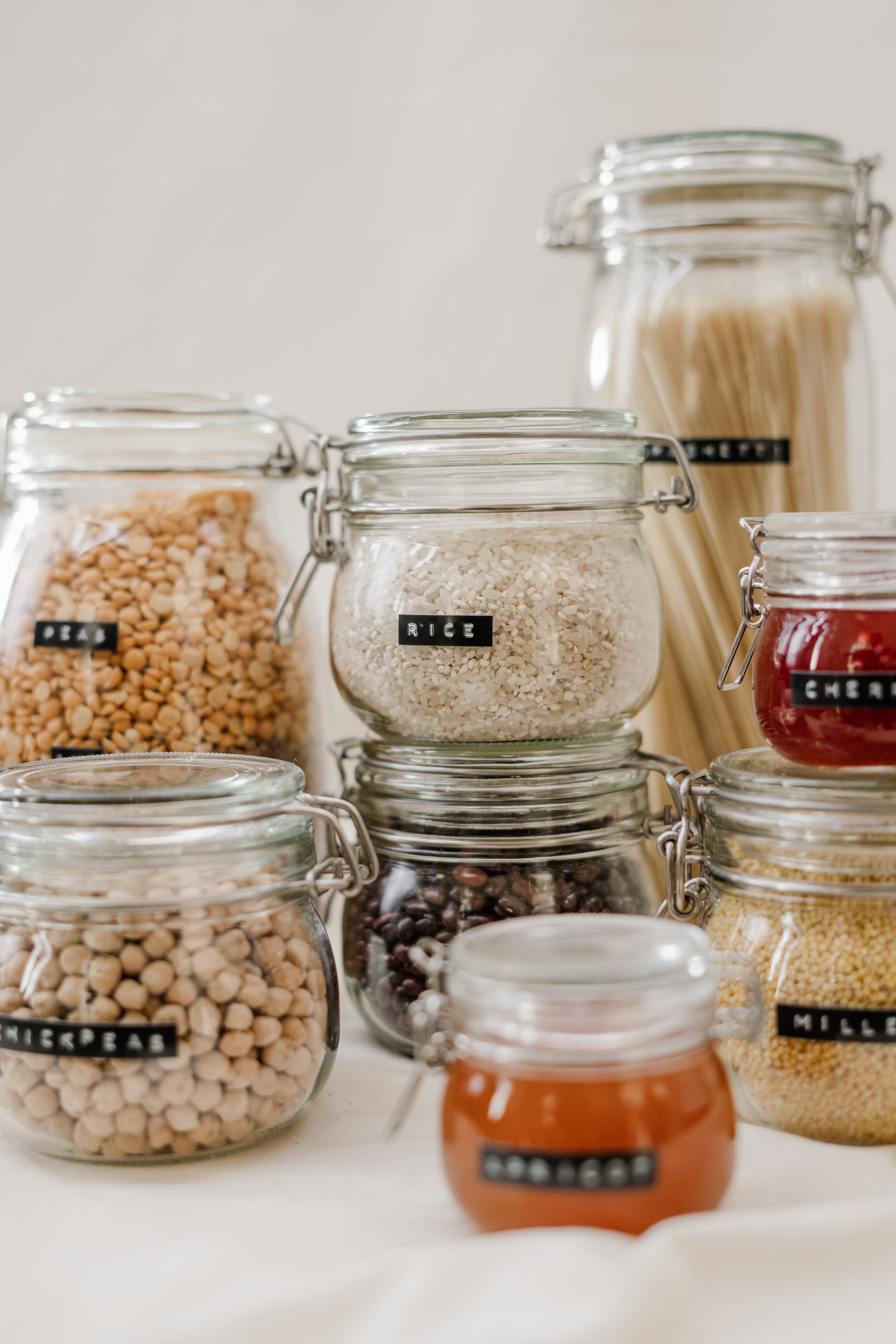
Canned and preserved goods:
– Soups, – cooking oil
– Canned beans and legumes, – Jams, jellies and preserves
Grains and cereals:
– Rice (white, brown, basmati, etc.)
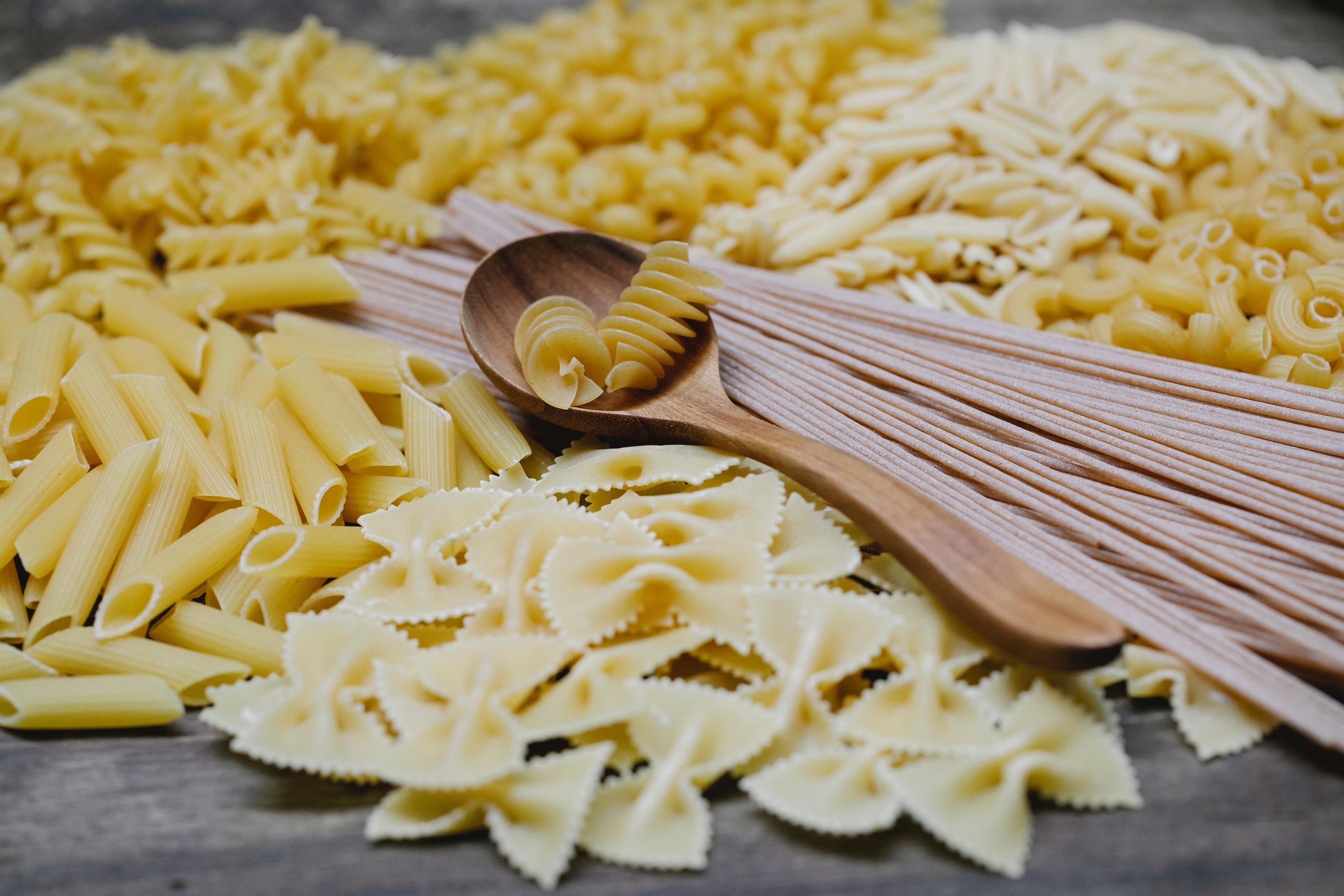
– Pasta, – Bread, – Oats, – Breakfast cereals
Baking supplies:
– Flour (all-purpose, whole wheat, etc.)
– Sugar, – Baking powder and baking soda, – Yeast
Spices and sauces:
– Ketchup, – Mustard
– Mayonnaise, – Salad item, – Soy sauce
Snacks and treats:
– Chips, – Crackers
– Cookies, – Nuts, – Candy
Beverages:
– Water, – Juice
– Soft drink, – Coffee, – Tea
Household items:
– Cleaning supplies (detergent, dish soap, etc.)
– Trash bags, – Storage bags
Personal care products:
– Soap and face wash
– Shampoo and conditioner
– Toothpaste
– Deodorant
– Razors
etc.

Fill this form




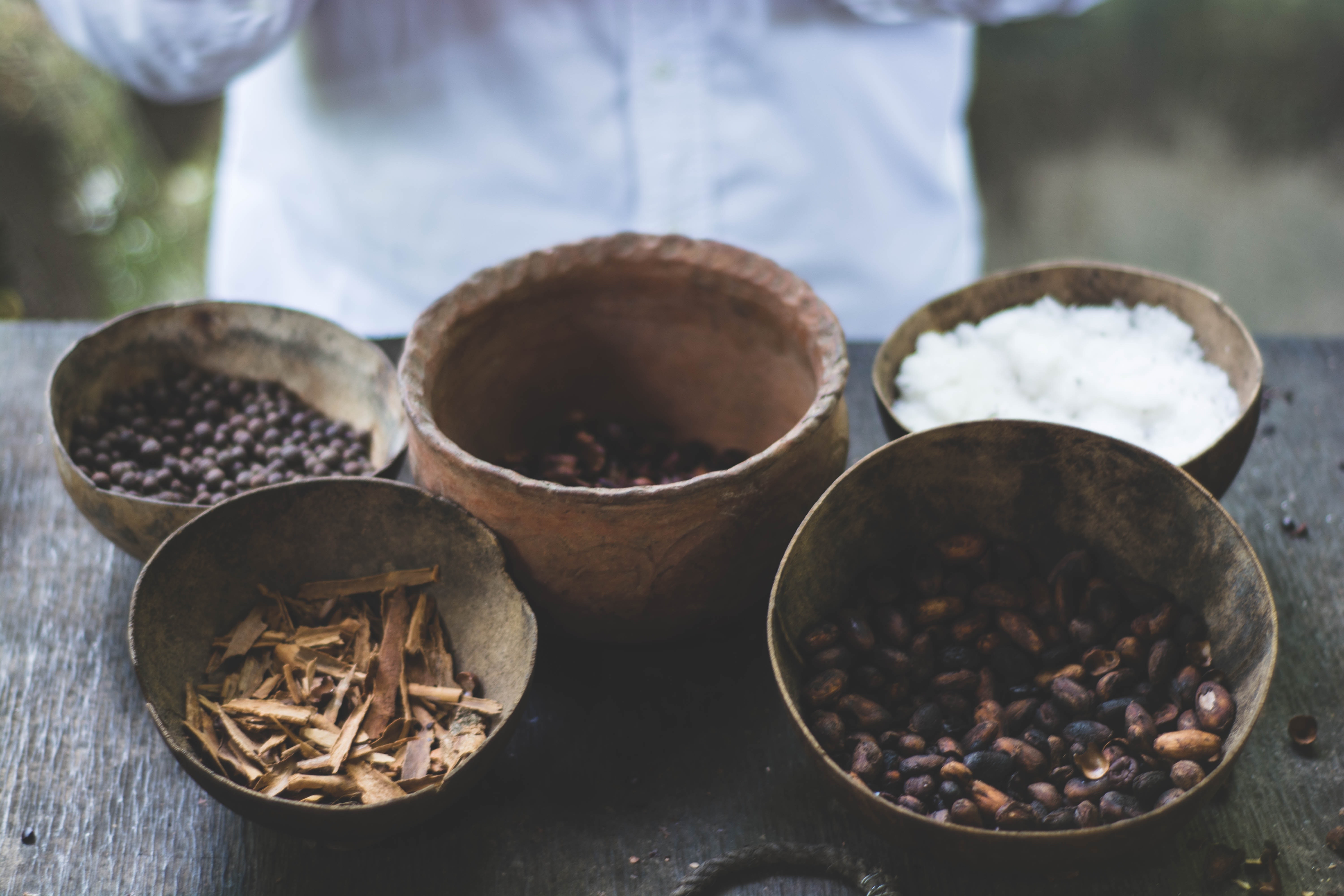
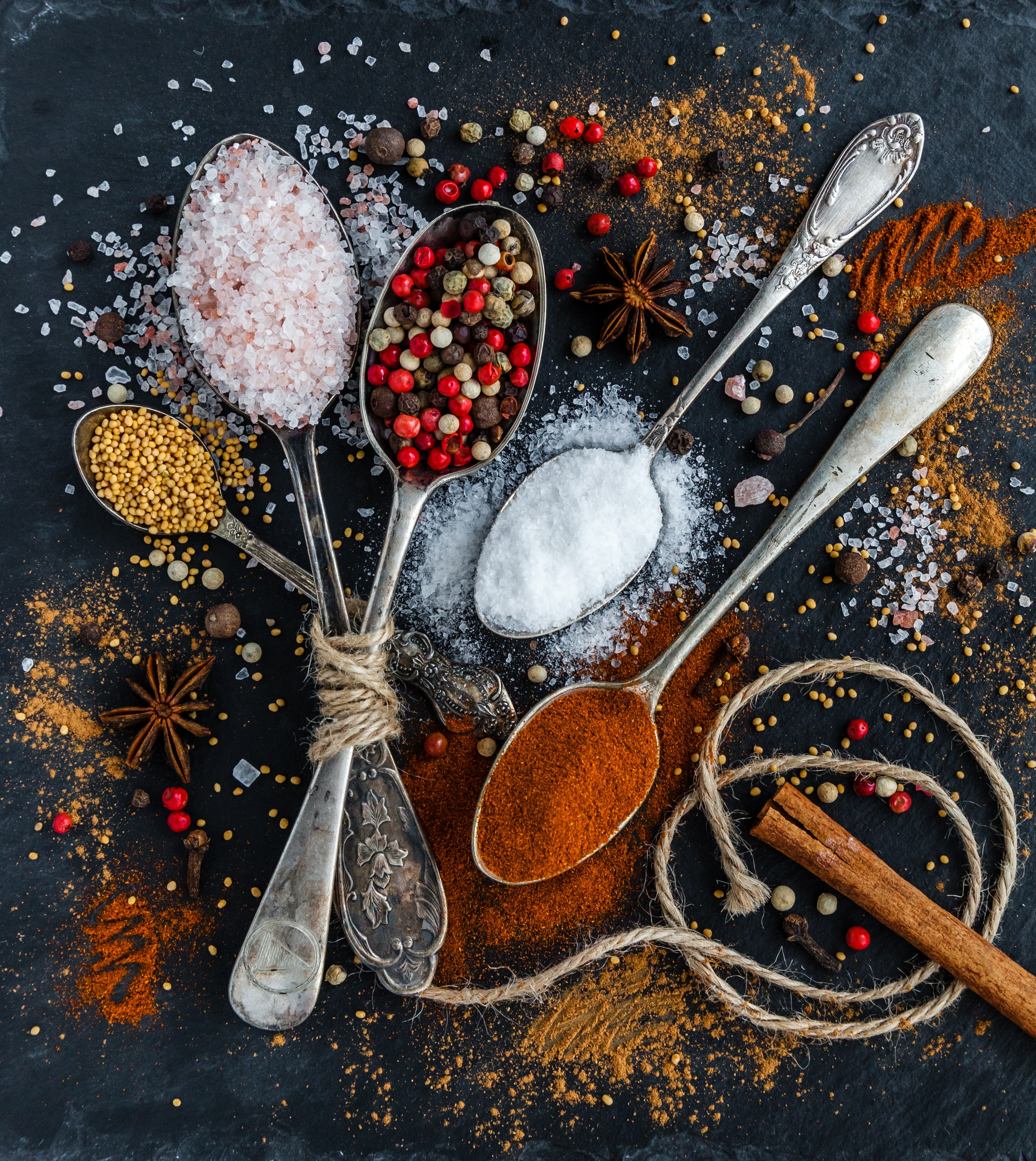
Spices are natural plant-based substances that are used to enhance the flavor, aroma, and appearance of food. They are derived from various parts of plants, such as seeds, bark, roots, fruits, or leaves, and are often dried and ground into powder form. Spices have been used for thousands of years to add depth and complexity to culinary preparations.
Spices are known for their distinctive flavors and can range from mild and aromatic to hot and pungent. They are used in cooking to season dishes, create unique flavor profiles, and elevate the overall taste experience. Additionally, spices can also contribute to the visual appeal of food by adding color and texture.
Different cultures and cuisines have their own unique spice blends and combinations, resulting in a diverse range of flavors around the world. Some commonly used spices include cinnamon, cumin, turmeric, ginger, cloves, paprika, cardamom, and many more.
Spices not only add taste and aroma to food but can also have health benefits. Many spices contain bioactive compounds with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties that can support overall well-being when consumed in moderation.
Overall, spices are an integral part of culinary traditions and play a crucial role in creating delicious and diverse dishes from around the globe.



India and Spice relation:
India and spices have a deep-rooted and inseparable connection that spans thousands of years. The country’s relationship with spices is not only culinary but also cultural, economic, and historical. India has been a hub for the production, trade, and consumption of spices since ancient times, and its influence on the spice trade has shaped the course of history. This essay will delve into the rich and multifaceted relationship between India and spices, highlighting their significance in various aspects.
India is often referred to as the “Land of Spices” due to its abundant variety and usage of spices. The country boasts a diverse climate and geography, which has enabled the cultivation of a wide range of spice crops. From the fragrant cardamom fields of Kerala to the fiery chili farms of Andhra Pradesh, India’s diverse regions offer the ideal conditions for growing an array of spices.
The history of spice usage in India dates back to ancient times. Indian spices such as black pepper, cinnamon, turmeric, and ginger were highly valued and sought after by traders from around the world. The spice trade played a significant role in connecting India with the rest of the world, leading to cultural exchanges, economic growth, and even colonization.
During ancient times, Indian spices were not only used for culinary purposes but also for medicinal and religious practices. Ayurveda, the traditional Indian system of medicine, incorporates various spices for their therapeutic properties. Spices were believed to have healing and health-promoting effects, and their usage in Ayurvedic remedies became deeply ingrained in Indian culture.
The spice trade became a lucrative business for India, attracting merchants from different parts of the world. Arab traders were the first to establish direct trade routes with India, followed by European powers like the Portuguese, Dutch, and British. The demand for Indian spices, particularly pepper, cloves, and cardamom, skyrocketed in Europe during the Middle Ages, leading to the exploration of sea routes to India. These explorations, such as Vasco da Gama’s voyage, eventually paved the way for European colonization of India.



The arrival of European powers in India not only influenced its spice trade but also left a lasting impact on its history. The Portuguese, Dutch, and British East India Companies established trading posts and forts along the coastal regions of India, primarily to control and monopolize the spice trade. These colonial powers exploited India’s spice resources, leading to the economic and political subjugation of the country.
However, the colonial period also had its positive effects on India’s spice industry. The British introduced modern agricultural practices, improved transportation infrastructure, and established spice plantations, which led to increased production and quality control. They also documented the botanical and culinary aspects of Indian spices, contributing to the knowledge and appreciation of spices worldwide.
Indian cuisine owes much of its vibrant and aromatic flavors to the skillful use of spices. Spices are the heart and soul of Indian cooking, adding depth, complexity, and a distinct character to various dishes. Each region in India has its own unique spice blends and cooking techniques, resulting in a diverse culinary tapestry. From the delicate biryanis of Lucknow to the fiery curries of South India, spices play a central role in defining the regional identities of Indian cuisine.
Indian spices have also found their way into the global culinary scene, influencing and enriching cuisines worldwide. The popularity of Indian food has led to the global demand for spices like cumin, coriander, turmeric, and fenugreek. These spices are now integral ingredients in international dishes, and their availability in supermarkets around the world testifies to India’s influence on the global spice market.
The economic significance of spices in India cannot be overlooked. Spices contribute to the country’s agricultural exports and provide employment opportunities for millions of farmers and laborers. India is one of the world’s largest producers and exporters of spices, accounting for a significant share of the global spice trade. Spices like cumin, chili, turmeric, and cardamom are major contributors to India’s agricultural exports, generating substantial revenue for the country.
Beyond culinary and economic aspects, spices have cultural and religious significance in India. They are used in religious rituals, festivals, and traditional ceremonies. Spices like turmeric and vermilion hold symbolic importance and are used for auspicious occasions and rituals. Spices also find their way into traditional art forms, literature, and folklore, further emphasizing their cultural significance.
In recent years, there has been a growing appreciation for the health benefits of Indian spices. Modern research has confirmed the medicinal properties of spices like turmeric, ginger, cinnamon, and cloves. These spices are known for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties, which have led to their integration into alternative medicine and dietary practices worldwide.
In conclusion, the relationship between India and spices is deep-rooted, multifaceted, and spans centuries. India’s diverse climate and geography have made it a fertile land for the cultivation of a wide variety of spices. The spice trade played a crucial role in connecting India with the world and shaping its history. Spices are integral to Indian cuisine, culture, economy, and even religion. India’s spices have influenced global culinary traditions and continue to be in high demand worldwide. With its rich heritage and ongoing contributions to the spice industry, India’s association with spices remains enduring and significant.





Benefits:
Spices offer a wide range of benefits, enhancing the taste of dishes while providing various health advantages. Here is a brief explanation of the many benefits of spices:
Flavor Enhancement: Spices add depth, complexity, and richness to food, making it more enjoyable and satisfying.
Antioxidant Powerhouse: Many spices are loaded with antioxidants, which help protect the body’s cells from damage caused by free radicals. Antioxidants play a crucial role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases and promoting overall health. Turmeric, cinnamon, cloves, and oregano are examples of antioxidant-rich spices.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Inflammation is a natural response by the body, but chronic inflammation can contribute to various health issues. Several spices possess anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the body. Turmeric, ginger, cayenne pepper, and cinnamon are known for their anti-inflammatory effects.
Digestive Aid: Spices have been used for centuries to aid digestion. They stimulate the production of digestive enzymes, promote bile flow, and increase gastric motility, which aids in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients. Ginger, fennel, coriander, and cumin are examples of spices with digestive benefits.
Metabolism Boost: Some spices have thermogenic properties, meaning they can increase metabolism and promote weight loss. They achieve this by boosting the body’s energy expenditure and fat-burning capabilities. Cayenne pepper and black pepper contain a compound called capsaicin, which is known to boost metabolism and increase fat burning.
Blood Sugar Regulation: Spices can have a positive impact on blood sugar control. Certain spices, such as cinnamon and fenugreek, have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. This can be beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
Heart Health: Spices have been linked to heart-protective effects. Garlic, for example, has been shown to help lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and improve overall cardiovascular health. Turmeric may also have positive effects on heart health by reducing inflammation and improving blood vessel function.
Immune System Support: Many spices possess antimicrobial and immune-boosting properties. Garlic, ginger, and cayenne pepper are known for their immune-enhancing effects, helping to fight off infections and support overall immune function.
Cognitive Function: Some spices have been associated with improved brain health and cognitive function. Turmeric, due to its active compound curcumin, has been studied for its potential to protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and improve memory and cognition.
Respiratory Health: Certain spices have traditionally been used to relieve respiratory issues. Cloves and cinnamon, for example, have been known to possess expectorant properties and can help alleviate coughs and congestion.
Pain Relief: Some spices, such as ginger and turmeric, have analgesic properties and may help alleviate pain and discomfort. They can be particularly useful for relieving joint pain and inflammation associated with conditions like arthritis.
Nutrient Boost: Spices are not only flavorful but also a source of various essential nutrients. They can contribute to the overall nutritional intake, providing vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber that are essential for optimal health.
Anti-Cancer Potential: Certain spices, such as turmeric and ginger, have shown promising anti-cancer properties in studies. They contain compounds that can inhibit the growth of cancer cells, reduce inflammation, and act as antioxidants, reducing the risk of certain types of cancer.
Mood Enhancement: The flavors and aromas of spices can stimulate the senses and positively impact mood and emotional well-being. Some spices, such as saffron, have even been studied for their potential antidepressant effects.
Dental Health: Spices like clove and cinnamon possess antimicrobial properties that can help fight bacteria and promote oral health. They can be beneficial in maintaining healthy teeth and gums.
Skin Health: Some spices have been used in traditional skincare remedies for their potential anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. Turmeric and cinnamon, for example, have been used to treat acne and improve skin complexion.
Detoxification: Spices like cumin, coriander, and ginger can support the body’s natural detoxification processes. They can aid in the elimination of toxins and promote overall detoxification.
Anti-Aging Effects: The high antioxidant content of certain spices may help protect against age-related damage caused by free radicals. They can help reduce the signs of aging and contribute to a more youthful appearance.
Food Preservation: Spices have been used for centuries as natural food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, extending the shelf life of food.
Cultural Significance: Spices have played a significant role in culinary traditions, cultural practices, and medicinal systems throughout history. They add diversity and richness to global cuisine, connecting people to their cultural heritage.
Incorporating a variety of spices into your meals can not only elevate the taste but also provide numerous health benefits. However, it is important to use spices in moderation and be aware of any allergies or sensitivities. Enjoy exploring the world of spices and their diverse benefits!

